Paid online consultations are available by appointment. For booking, please contact us via Whatsapp.
Epilepsy Surgery
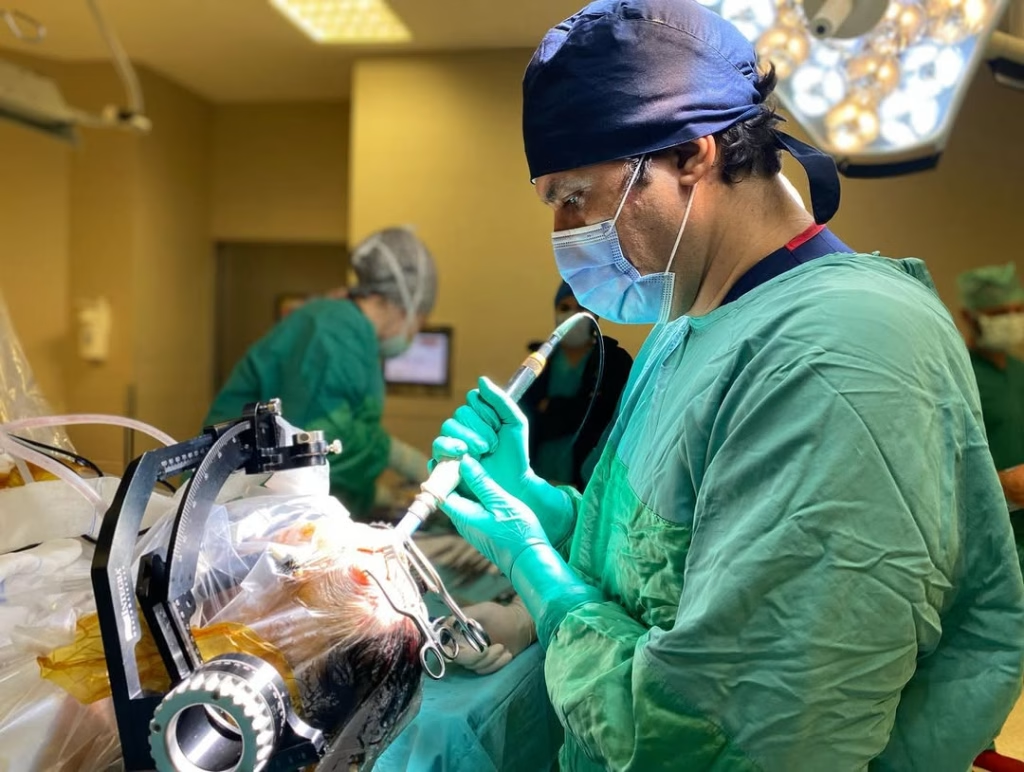
Epilepsy Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide to a New Beginning
Epilepsy surgery can be a life-changing option. It offers hope for a future with fewer or no seizures. This guide explores the details of this advanced treatment. We will discuss who is a candidate for this procedure. We will also cover the types of surgeries available. Our goal is to provide clear and helpful information. This helps you make informed decisions about your health. Understanding your options is the first step toward control.
Last reviewed: 29 October 2025 • Evidence‑based content • Patient‑centered language
Understanding Epilepsy and When to Consider Surgery
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder. It causes recurrent, unprovoked seizures. These seizures are sudden bursts of electrical activity in the brain. For many people, medication effectively controls these episodes. However, some individuals do not respond to anti-seizure drugs. Their condition is known as drug-resistant epilepsy. This is when surgery becomes a potential path forward. It is a significant step towards a better quality of life.
What is Drug-Resistant Epilepsy?
You may have drug-resistant epilepsy. This happens if you have tried two or more medications. These medications did not control your seizures. This condition can be challenging. It affects daily life and overall well-being. Therefore, exploring other treatments is crucial. Epilepsy surgery is a powerful alternative in these cases. It directly addresses the source of the seizures in the brain.
Are You a Candidate for Epilepsy Surgery?
Deciding on surgery is a major step. A team of specialists helps make this decision. Neurosurgeons, neurologists, and other experts work together. They carefully check if surgery is right for you. They perform a detailed evaluation. This process ensures the surgery is both safe and effective for your specific case. Your health and safety are the top priority.
The Comprehensive Evaluation Process
The evaluation for epilepsy surgery is thorough. It involves several advanced tests. These tests pinpoint the exact location of seizure origin. This specific area is called the seizure focus.
Key evaluation steps may include:
- Video-EEG Monitoring: This test records your brainwaves during a seizure. It helps doctors see where seizures start.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): A brain MRI creates detailed images. It can show abnormalities that might cause seizures.
- PET and SPECT Scans: These scans show brain activity. They help find the seizure focus.
- Neuropsychological Testing: This assesses your memory and thinking skills. It provides a baseline before surgery.
These tests help the medical team create a precise surgical plan. For more information on diagnosis, you can consult resources like the World Health Organization (WHO).
Types of Epilepsy Surgery Explained
There are several types of epilepsy surgery. The best type for you depends on your specific condition. Your surgical team will recommend the most suitable approach. Their goal is to maximize seizure control. They also aim to minimize risks.
Resective Surgery: Removing the Seizure Source
Resective surgery is the most common type. Surgeons carefully remove the small area of brain tissue. This is the area where your seizures originate. The goal is to remove the source without harming vital functions. For example, temporal lobectomy is a common resective surgery. It has a high success rate for temporal lobe epilepsy. Technology like intraoperative mapping helps protect critical brain areas.
Disconnection Surgery: Interrupting Seizure Pathways
Sometimes, the seizure focus cannot be removed. It may be in a critical brain area. In these cases, disconnection surgery is an option. Surgeons cut the nerve pathways that seizures use to spread. A corpus callosotomy is one example. It prevents seizures from moving between the two halves of the brain. This can make seizures less severe.
Neuromodulation: Regulating Brain Activity
Neuromodulation is a newer approach. It does not involve removing brain tissue. Instead, it uses devices to regulate brain activity. These devices can reduce seizure frequency and severity.
Popular neuromodulation therapies include:
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): A small device is implanted in the chest. It sends mild electrical pulses to the brain via the vagus nerve.
- Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS): A device is placed in the skull. It monitors brain activity and delivers stimulation to stop seizures before they start.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Electrodes are placed deep in the brain. They send continuous electrical signals to regulate brain function.
These therapies are excellent options for people who are not candidates for resective surgery.
What to Expect: The Surgical Journey
The journey through epilepsy surgery involves several phases. Your medical team will guide you at every step. They provide support and answer your questions. Understanding the process can help reduce anxiety.
Before the Procedure
Before surgery, you will meet with your neurosurgeon. You will discuss the procedure in detail. They will explain the goals and potential risks. You will also receive instructions on how to prepare. This may include stopping certain medications. You should arrange for someone to help you during recovery. Proper preparation is key to a smooth experience.
After the Surgery and Recovery
After the procedure, you will stay in the hospital. The medical team will monitor your recovery closely. The length of your stay depends on the type of surgery. Recovery at home continues for several weeks. You will need to rest and follow your doctor’s instructions. Physical therapy may be part of your recovery plan. Gradual return to normal activities is important. Patience is essential during this period.
Risks and Benefits of Epilepsy Surgery
Every surgery has risks and benefits. It is important to weigh them carefully. Your doctor will discuss these with you.
Potential Benefits:
- Significant reduction or complete elimination of seizures.
- Improved quality of life and independence.
- Potential to reduce or stop anti-seizure medication.
- Better memory and cognitive function in some cases.
Potential Risks:
- Risks associated with any brain surgery, like infection or bleeding.
- Changes in mood, memory, or personality.
- Neurological deficits, which are often temporary.
- The surgery may not be successful in controlling seizures.
A detailed discussion with your neurosurgeon is vital. They can explain the risks specific to your case.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Epilepsy Surgery
Q1: How successful is epilepsy surgery?
The success rate varies. It depends on the type of surgery and the individual. For some resective surgeries, over 70% of patients become seizure-free. Your doctor can give you a more personalized outlook.
Q2: How long is the recovery period?
Hospital recovery is typically a few days. Full recovery at home can take one to three months. It depends on the surgery and your overall health.
Q3: Will I be able to stop my medication after surgery?
Many patients can reduce their medication. Some can stop it completely over time. However, this decision must be made with your doctor. Do not stop medication on your own.
Q4: What are the main risks of the surgery?
The primary risks involve infection, bleeding, and potential changes to neurological functions like memory or vision. Advanced surgical techniques help minimize these risks significantly.
Q5: Is epilepsy surgery painful?
You will be under general anesthesia during the surgery. You will not feel any pain. After the procedure, pain medication is used to manage any discomfort. Most patients report manageable pain levels.
Take the Next Step Towards a Seizure-Free Life
If you believe you are a candidate, you should contact a specialist for a consultation. Taking the next step can open the door to a new life free from the limitations of seizures. The journey starts with a conversation.
Book an AppointmentVisit our Contact page for more ways to get in touch.
Peripheral Nerve Entrapment and Carpal Tunnel: A Complete Guide to Recovery
Do you wake up at night because of numbness in your hands? Or perhaps you feel the need to “shake” your hands in the morning.
January 8, 2026
No Comments
What is Craniopharyngioma?
Facing a brain tumor diagnosis is undoubtedly tough. For instance, as a patient or relative, you are likely living through a challenging moment. Currently, you
January 7, 2026
No Comments
Metastatic Brain Tumors: Comprehensive Diagnosis, Treatment, and Survival Guide
Receiving a cancer diagnosis is undoubtedly one of the most challenging turns in your life. Honestly, hearing terms like “spread to the brain” or medically
December 31, 2025
No Comments

Meningioma: Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Receiving a diagnosis of a brain tumor is frightening. However, knowledge is power. Meningioma is the most common type of primary brain tumor. Understanding this
December 31, 2025
No Comments
Brain Tumour Symptoms: Early Diagnosis and Modern Treatment Methods
The brain is the most complex organ in our body. It controls all our movements, emotions, and thoughts. So, what happens when uncontrolled cell growth
November 28, 2025
No Comments
Skull Base Tumor
A skull base tumor is a complex health issue. It is located at the base of the skull. This vital area protects the brain. Furthermore,
November 26, 2025
No Comments

